What Is Damp Proofing?
It might be quite clear as to what damp proofing is, but knowing the ins and outs of this essential process could serve you well. At its core, damp proofing is a way to protect your property from water getting into its walls, floors, and foundations. This is achieved by installing barriers or applying specific treatments.
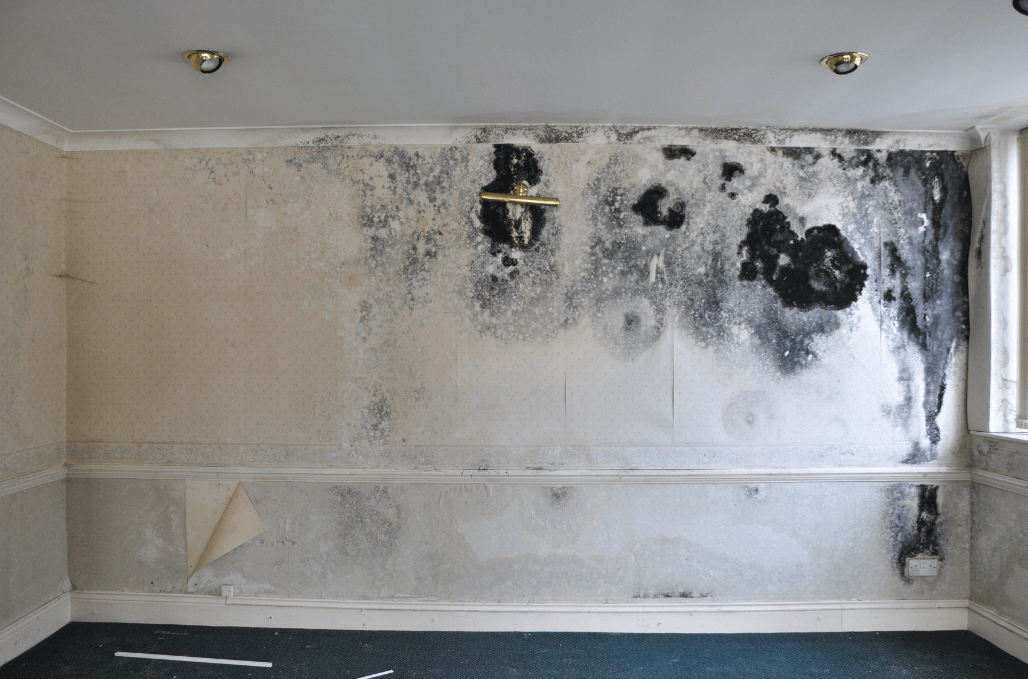
Penetrating damp, rising damp, and condensation can cause serious issues, including crumbling plaster, mould growth, and weakened masonry walls in your home.
Improper damp proofing can reduce your home’s value, lead to increased heating costs, and even cause health risks. A well-executed damp proofing process ensures that moisture rising from the ground or water seeping through external walls is stopped, leaving your property dry and protected.
What Are The Different Types Of Damp?
- Rising Damp: Caused by moisture moving upwards from the ground through porous materials such as bricks. It can leave tidemarks or staining on walls.
- Penetrating Damp: Water seeping through the external wall, often caused by structural issues like cracks or faulty gutters.
- Condensation: Excess moisture in the air condenses on cold surfaces like windows or walls, leading to mould and damp areas.
Each type of damp requires specific treatments. To fully understand which type of damp is affecting your property, a damp proofing survey is recommended.
Why Is Damp Proofing Essential?
Damp walls often have discolouration and stains, which make them unsightly. But, more importantly the dampness in the affected walls can cause costly damage to a building.
Untreated damp makes walls cold and reduces the effectiveness of insulation. This loss means it can cost more to heat your home.
Damp walls are an ideal breeding ground for mould and mildew. Again, not only does this not look great it can lead to severe health risks including respiratory illnesses and allergies.
If damp proofing is not installed or is installed incorrectly, it can lead to increasingly costly upkeep and remediation.
What Materials Are Used in Damp Proofing?
The materials used for damp treatment vary depending on the method and the type of damp being treated. Below are some of the most common materials:
Physical Barriers
Bitumen Felt: A waterproof material used in damp-proof courses and membranes. Its durability makes it ideal for long-term protection.
Plastic Sheeting: High-density polyethylene or polypropylene is often used for damp proof membranes, particularly in basements and ground floors.
Slate: Found in older properties, slate was historically used as a physical damp-proof course due to its impermeability.
Metal Sheets: Non-corrosive metals like lead or copper can be used as a damp proof course in specific scenarios.
Chemical Treatments
Silicone-Based Injections: These are injected into walls and floors to form a water-repellent barrier, effectively stopping rising damp.
Acrylic Gels: Used for waterproofing and creating a moisture barrier within the masonry.
Additives in Concrete: Integral damp proofing involves mixing waterproofing agents directly into concrete during construction.
Coatings and Sealants
Cementitious Waterproofing: A cement-based coating applied to external walls or foundations to prevent water penetration.
Breathable Sealants: Protect masonry walls from rainwater while allowing trapped moisture to evaporate.
Types of Damp Proofing
Physical Damp Proof Course
A physical damp proof course is a durable barrier installed in walls to block water from rising. It is typically made from slate, bitumen, or plastic. This feature is standard in modern construction. Still, many older homes lack this protection, making them susceptible to rising damp.
Chemical Damp Proofing
A chemical damp proof course is used in properties where installing a physical barrier is not feasible. It involves injecting a silicone-based solution into the wall at regular intervals. This chemical forms a water-repellent layer within the masonry, stopping moisture from travelling upwards. This is a popular method for tackling rising damp problems in older buildings.
Damp-Proof Membrane
A damp proof membrane (DPM) is a flexible, impermeable sheet installed on walls or floors to block moisture. It is commonly used in basements and areas below ground level, where ground-level moisture is a persistent issue. Damp-proof membranes are often used with other methods like chemical injections to provide comprehensive protection.
Integral Damp Proofing
This method involves adding waterproofing agents directly to concrete during construction. These additives make the concrete resistant to moisture ingress, offering long-term protection for walls and floors. Integral damp proofing is often used in the foundations of modern buildings.
Electro-Osmotic Damp Proofing
This method uses electrical currents to repel water from the walls. Electrodes are inserted into the masonry, and a low-voltage current is applied, changing the direction of water movement and stopping damp from the ground from rising. This technique is less common but can be highly effective in some instances.
The Damp Proofing Process
Our damp proofing process is meticulous – we ensure all sources of damp are identified and treated effectively. Below is an in-depth look at the steps involved:
Step 1: Damp Survey
APP’s damp proofing surveyor inspects your property to diagnose the damp and its severity. We’ll look for signs of damp, including damp patches, peeling paint, tide marks, and mould. The survey also identifies whether the issue is rising damp, penetrating damp, or condensation.
We use bespoke tools like moisture meters to measure the damp levels within masonry walls and determine the best course of action. This step is crucial, as misdiagnosing the damp issue can lead to ineffective treatments.
Step 2: Preparing the Property
Before we apply any damp-proofing treatments, we advise on how external factors contributing to the problem must be resolved. These might include:
- Fixing cracks in external walls or damaged mortar.
- Clearing and repairing gutters or downpipes to prevent water overflow.
- Ensuring proper drainage to divert water away from the foundation.
By doing this, we make sure the source of the damp is addressed, preventing recurring problems.
Step 3: Damp-Proofing Application
- Once the property is prepared, we begin to apply the most appropriate damp-proofing method:
- Physical Damp-Proof Course Installation: A barrier is embedded into the walls to block moisture rising.
- Chemical Damp Proofing: Holes are drilled at intervals, and a chemical solution is injected to form a moisture-resistant barrier.
- Damp-Proof Membranes: These are installed on walls and floors, especially in basements, to block moisture from entering the property.
Step 4: Internal Restoration
After damp-proofing treatments are complete, we will repair the damaged interior. This can involve removing plaster affected by salts and moisture, by replacing it with a salt-resistant render. We then make good the walls ready for redecorating. We can also treat mould and other stains to prevent recurrence.
Step 5: Post-Treatment Maintenance
Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure the damp-proofing work remains intact. Homeowners should:
- Inspect gutters and drainage systems regularly to prevent water ingress.
- Improve ventilation in areas prone to condensation, such as kitchens and bathrooms.
- Monitor internal walls and floors for any signs of damp, acting quickly to address new issues.
How Much Does Damp Proofing Costs
The cost of damp proofing varies depending on the property size, the damp, and the treatment required. Typical costs include:
- Chemical Damp-Proof Course: £1,000–£2,500 for a medium-sized property.
- Damp-Proof Membrane: £3,000–£5,000 for a basement.
- Physical DPC: £1,500–£3,000 for retrofitting.
While DIY solutions are available, we would always recommend hiring a professional damp proofing specialist. Specialists such as APP have the knowledge and tools to properly diagnose and effectively treat damp issues.
What is The Difference Between Damp Proofing and Water Proofing?
Damp proofing and waterproofing are often confused but serve different purposes in property maintenance. Damp proofing primarily addresses existing damp issues by preventing moisture from penetrating walls through methods like damp proof courses.
This includes various types, such as remedial damp proof courses and damp proof injections. On the other hand, waterproofing is a more extensive process that protects against water ingress, often involving membranes to create a barrier against water from the ground.
Key Takeaways If You Have Signs Of Damp Problems
Effective damp proofing requires an accurate diagnosis and expert application. A professional damp specialist ensures that the underlying cause of your damp is addressed, not just the symptoms. They use specialist materials like chemical damp proof courses, membranes, and waterproof coatings to provide long-lasting protection. Attempting to tackle damp issues without professional expertise can lead to incomplete solutions and recurring problems.
Proper damp proofing restores your property and prevents future damage, ensuring a safe, dry, and energy-efficient home.
We’re Ready To Help You
Please get in touch with our friendly team today and we can get the ball rolling on your project sooner than you think.