What Are Ground Gases?
Ground gas is becoming an expanding problem in the UK and is being recognised more and more by professional contractors and homeowners alike. Ground gases are gases that either occur naturally in the ground or as a byproduct of human activity. Dumping, landfilling and mining are major causes of pollution and harmful ground gas build up.
Ground gases can include such vapours as methane, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and volatile compounds (VOCs). These gases can work their way through subsoil and then cracks and fissures into buildings themselves.
how do ground gas occur?
Ground gas can occur naturally through coal bearing strata, bedrock containing uranium, limestone and organic sediments such as peat and alluvium. However, it is more likely that ground gases will occur through human activity in the form of pollution. These ground gases occur through landfill, made up ground, mining and past contaminative activity.
What Ground Gases are there?
There are many naturally occurring and pollutant gases that can cause problems, for example VOCs occurring as a result of petrol, oil or solvent spillages. Gases produced by the action of microorganisms on biodegradable waste materials in landfills. Coal mining areas can have raised levels of carbon dioxide and nitrogen. Organic-rich sediments, such as peat, are prone to leaking methane and carbon dioxide.
The Different types of ground gases that occur include:
- Radon
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Carbon Monoxide
- Nitrogen
- Methane (CH4)
- Hydrogen Sulphide
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
When did ground gas become an issue?
In the past, ground gases were not perceived as an issue that needed much additional thought. This outlook has changed over the years partly due to the increased need for housing in the UK and the subsequent requirement for land to develop on. The pressure on finding suitable land has led to rapid growth of development on “brownfield” sites. Brownfield sites are areas of previously developed land that often contain pollutants affecting the ground soil.
Increased risk of brownfield development and raised awareness has driven the Environment Agency to deliver new legislation that has been adopted by local authorities. This legislation takes a far more strict approach to matters of ground gas risk.
is ground gas a hazard?
Ground gases, whether naturally occurring or from other means, can be odorous, toxic, asphyxiating, flammable and explosive. These potential hazards could be present on any new or existing development that has yet to be surveyed. It is recommended that sites be investigated for ground gas contamination risk and, if necessary, measures will need to be implemented to mitigate the risk.
How to protect buildings from ground gas
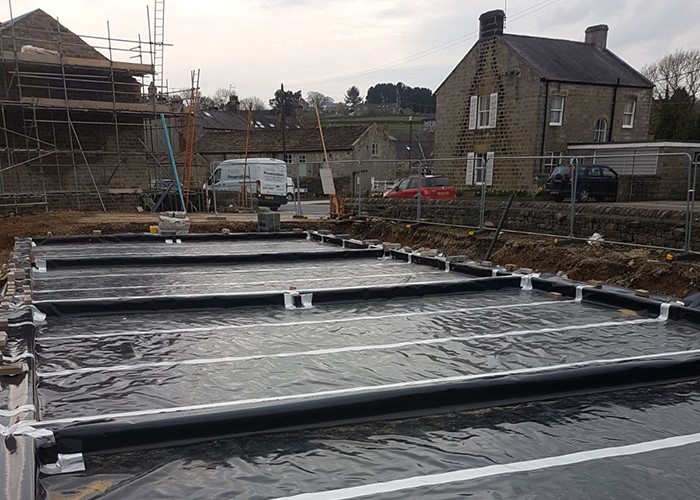
Gas protection measures are used to interrupt possible gas migration pathways, essentially stopping toxic, asphyxiating, flammable and potentially explosive gases entering a building. One of the most widely used options for protecting a building is gas membrane protection.
Gas membranes are typically plastic sheets that prevent ground gases from passing through them. Many gas membranes also act as a damp course membrane which protects buildings from ground gases and moisture. These ground gas membrane protection systems are usually installed during construction as part of the foundation design.
It is absolutely essential that gas membranes are installed correctly and they meet all applicable building standards and regulations. This is why we always recommend using a trusted contractor with decades of experience and a solid reputation across the Cambridgeshire region. APP is a professional installation specialist that understands the requirements of each specific project and can consult and install as needed.
We’re Ready To Help You
Please get in touch with our friendly team today and we can get the ball rolling on your project sooner than you think.